How to grow microgreens
Introduction
A Glimpse into the World of Microgreens
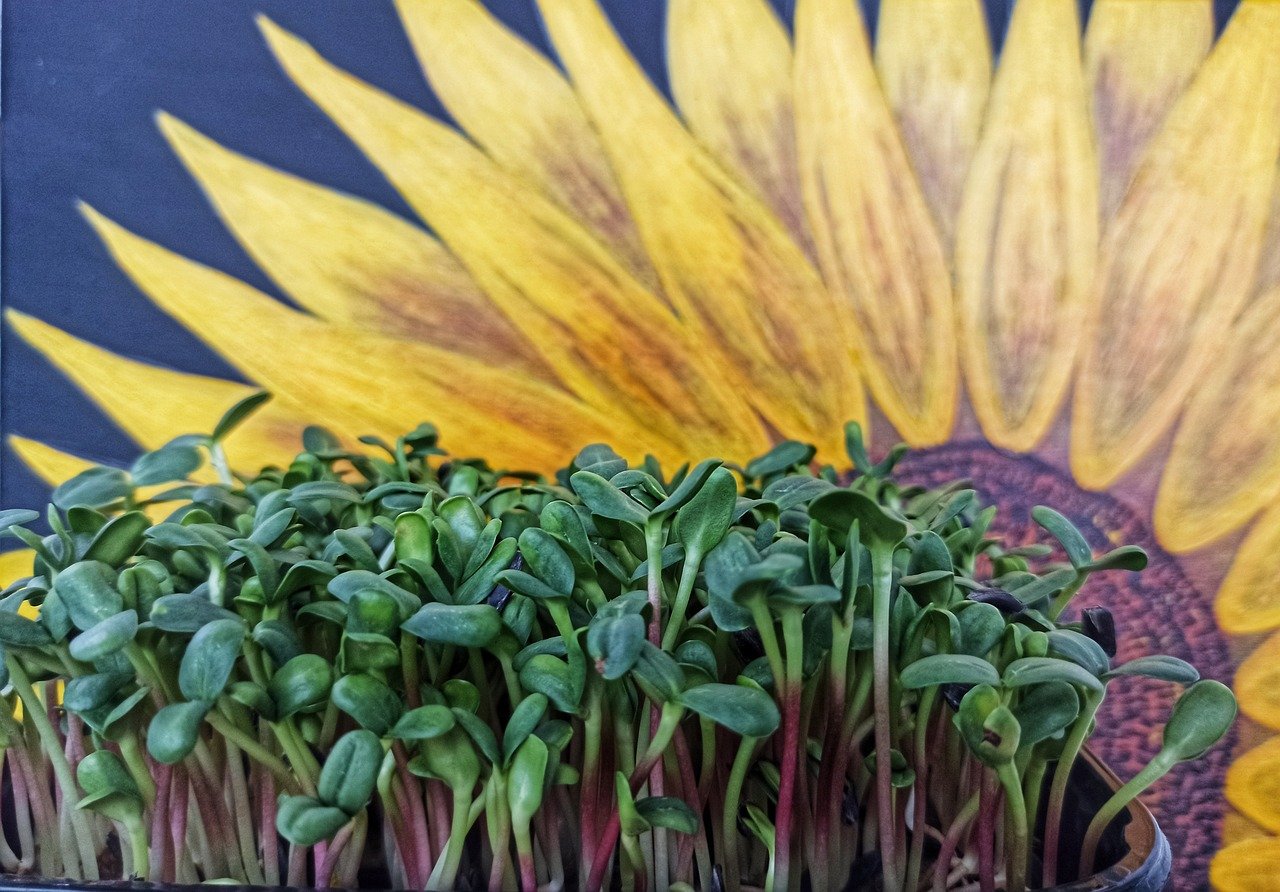
Microgreens, often touted as nature’s miniature marvels, are young vegetable greens harvested at an early stage of growth. These tiny greens burst forth with vibrant colors and pack a powerful punch in terms of flavor and nutrition.
Ranging from delicate pea shoots to robust radish microgreens, these petite plants offer a concentrated dose of essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Their popularity has surged in recent years due to their versatility in culinary creations and their reputation as nutrient powerhouses.
The Bounty of Benefits

Beyond their visual appeal and gastronomic allure, microgreens boast an impressive array of health benefits that make them a must-have for any aspiring home gardener or culinary enthusiast. Studies have shown that microgreens can contain up to 40 times more nutrients than their mature counterparts. From boosting immunity to promoting healthy digestion, these mini greens are a nutritional dynamo.
Additionally, growing microgreens at home provides a sustainable source of fresh produce year-round, allowing individuals to take control of their food sources and reduce waste. Embracing the art of cultivating microgreens is not merely a hobby but a holistic journey towards wellness and self-sufficiency.
Introduction
Microgreens are young, edible seedlings harvested at an early stage of growth, typically within 7-21 days after sowing. These tiny greens pack a powerful punch of flavor and nutrients, making them a popular choice for culinary enthusiasts and health-conscious individuals alike. Despite their small size, microgreens are known to contain high concentrations of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, often surpassing the nutritional content of their mature plant counterparts.
Brief Overview of Microgreens
Microgreens encompass a diverse range of plant varieties such as kale, radish, arugula, and basil, each offering a unique flavor profile and nutritional composition. These miniature greens are harvested just above the soil line when their first true leaves emerge, providing a delicate texture and intense taste that can elevate any dish they adorn. With their vibrant colors and intricate shapes, microgreens not only enhance the visual appeal of culinary creations but also contribute to a delightful sensory experience.
Benefits of Growing Microgreens at Home
Growing microgreens at home offers numerous advantages beyond just culinary enjoyment. One significant benefit is the ability to have fresh access to these nutrient-dense greens year-round without relying on store-bought options that may have traveled long distances or been treated with chemicals.
Additionally, cultivating microgreens indoors provides a rewarding gardening experience regardless of space limitations since they can thrive in small containers or trays on windowsills or countertops. The cost-effectiveness of growing microgreens at home is another compelling reason to embark on this horticultural journey.
By producing your own microgreens from seeds at a fraction of the price compared to purchasing pre-cut varieties from grocery stores, you not only save money but also reduce food waste by harvesting only what you need when you need it. Furthermore, the satisfaction derived from nurturing these miniature plants from seed to harvest fosters a deeper connection to nature and promotes sustainable living practices in your daily routine.
Selecting the Right Seeds for Microgreens

When it comes to growing microgreens, selecting the right seeds is crucial for the success of your indoor garden. There are a plethora of popular varieties of microgreen seeds to choose from, each offering unique flavors and nutritional benefits.
Some common varieties include broccoli, radish, sunflower, kale, and arugula. These seeds can be easily found at local gardening stores or purchased online from reputable suppliers.
One important consideration when choosing microgreen seeds is whether to opt for organic or non-organic varieties. Organic seeds are grown without synthetic pesticides or fertilizers, making them a more environmentally friendly choice.
They also tend to yield microgreens that are free from harmful chemicals. On the other hand, non-organic seeds may be more affordable and readily available but could potentially contain traces of pesticides or other chemicals.
Choosing the Right Growing Medium
The choice of growing medium plays a significant role in the growth and development of your microgreens.
Two common options for growing microgreens are soil and hydroponic systems. Soil-based growing mediums provide essential nutrients for plant growth and mimic outdoor gardening conditions.
They can be a cost-effective option for beginners and offer good water retention properties. Alternatively, hydroponic systems involve growing plants in a nutrient-rich water solution without using soil.
This method can result in faster growth rates and efficient nutrient absorption by the plants. DIY enthusiasts may prefer to create their own hydroponic setups using simple materials like PVC pipes or aquariums, while pre-made kits provide an easy-to-use solution for those looking for convenience.
Planting and Germination

Preparing the Planting Trays or Containers
When it comes to growing microgreens, the choice of planting trays or containers plays a crucial role in ensuring successful germination and growth. It is essential to select trays that are clean, sterilized, and provide adequate drainage to prevent waterlogging. Opt for shallow containers to promote airflow around the seedlings and reduce the risk of mold or mildew formation.
Additionally, consider using trays with transparent covers or domes to create a mini greenhouse effect that retains moisture and warmth during the germination process. Before sowing the seeds, thoroughly clean and disinfect the planting trays to minimize the chances of contamination and ensure a healthy start for your microgreens.
Sowing the Seeds Evenly and Densely for Optimal Growth
Achieving uniform growth and a dense crop of microgreens begins with proper seed sowing techniques. When sowing seeds for microgreens, aim for an even distribution across the planting surface while maintaining a dense arrangement to maximize yield per tray.
Avoid overcrowding as this can lead to competition for resources among seedlings, resulting in stunted growth and poor development. Depending on the type of seeds used, follow specific guidelines regarding seed density per square inch to achieve optimal results.
Gently press down on the seeds after sowing them to ensure good contact with the growing medium without burying them too deeply. By mastering the art of sowing seeds evenly and densely, you set a solid foundation for vigorous germination and robust growth of your microgreens.
Care and Maintenance

Watering Schedule and Techniques to Prevent Mold or Overwatering
Proper watering is essential for the healthy growth of microgreens. Overwatering can lead to mold, root rot, and other issues, while underwatering can cause stunted growth. To prevent these problems, it’s crucial to establish a consistent watering schedule based on the type of microgreens you are growing and the environmental conditions they are in.
A general rule of thumb is to water your microgreens once or twice a day, ensuring that the soil remains consistently moist but not waterlogged. One effective technique to prevent mold is bottom watering, where you place your trays in a shallow tray of water allowing the soil to absorb moisture through the drainage holes at the bottom.
Additionally, using a spray bottle with a fine mist setting can help you water your microgreens gently without disturbing their delicate foliage. This method also helps maintain proper humidity levels around your plants, promoting healthy growth.
Always monitor the moisture level of your growing medium by gently pressing it with your finger – if it feels too wet or dry, adjust your watering schedule accordingly. Remember that different types of microgreens may have varying water requirements, so it’s essential to observe how each variety responds to watering and adjust as needed.
Providing Proper Ventilation to Avoid Humidity-Related Issues
Humidity levels play a significant role in the overall health of your microgreens. Proper ventilation is essential for preventing humidity-related issues such as mold growth and fungal diseases.
Adequate air circulation helps reduce excess moisture around your plants and minimizes the risk of damp conditions that favor pathogens. To ensure proper ventilation, consider placing a small fan near your growing area on low speed to promote air movement without causing stress to delicate seedlings.
Another effective way to improve ventilation is by spacing out your trays or containers appropriately to allow for airflow between them. Avoid overcrowding plants as this can create pockets of stagnant air conducive to humidity-related problems.
If you notice any condensation forming on surfaces inside your growing area, increase ventilation by opening windows slightly or using an exhaust fan if available. Regularly inspecting for signs of high humidity such as droplets on leaves or soggy soil can help you identify potential issues early on and take corrective measures promptly.
Practical Tips on Controlling Pests Naturally
Pests can pose a significant threat to your microgreen crop if left unchecked. However, immediately resorting to pesticides may not be ideal due to the potential harm they may cause to humans or animals. Natural methods of controlling pests are a preferred solution.
One effective approach is to introduce beneficial insects like ladybugs, lacewings, and predatory mites, which prey upon common garden pests such as aphids, whiteflies, and spider mites. Another technique involves physical removal by manually picking off larger insects or using sticky traps to catch flying pests.
Many gardeners also swear by homemade insecticidal soap spray. This mixture, diluted with liquid soap and warm water, acts as a contact pesticide that directly targets soft-bodied insects like aphids, caterpillars, and mealybugs. Using neem oil is another organic option that disrupts feeding habits and interferes with the life cycle of damaging larvae.
Other preventive measures include maintaining cleanliness around the growing area and removing fallen plant debris regularly to reduce hiding places for pests. Frequent inspection allows for early detection of potential infestations. Stay proactive by implementing these natural pest control methods to maintain a healthy, thriving microgreen crop.
Harvesting and Storage

Determining the Ideal Time for Harvesting Based on Seed Variety
Harvesting microgreens at the right time is crucial to ensure optimal flavor, texture, and nutritional content. The ideal harvesting time varies depending on the seed variety you are growing. Generally, most microgreens are ready to be harvested within 7-14 days after sowing, but some varieties may take longer.
To determine readiness for harvest, look for the development of true leaves beyond the cotyledon stage. The microgreens should be vibrant in color, with a good leaf-to-stem ratio.
Cutting Techniques to Preserve Plant Health
When it comes to harvesting microgreens, using proper cutting techniques is essential to promote continued growth and maintain plant health. Instead of pulling out the entire plant from the growing medium, it is recommended to use sharp scissors or a clean knife to cut the stems just above the soil level.
This method allows for regrowth and ensures that you can continue harvesting from the same batch of seeds multiple times. Avoid tearing or bruising the delicate leaves during cutting as this can reduce shelf life and compromise flavor.
Storing Harvested Microgreens to Maintain Freshness
After harvesting your microgreens, it is important to store them properly to maintain their freshness and quality. To extend shelf life, gently wash the harvested greens in cold water and pat them dry with a clean towel or use a salad spinner to remove excess moisture. Store the microgreens in airtight containers lined with paper towels or kitchen towels to absorb any remaining moisture that could lead to spoilage.
Place them in the refrigerator’s crisper drawer where they will stay fresh for up to a week. Remember that microgreens are best enjoyed fresh, so try to use them as soon as possible for optimal taste and nutrition.
Culinary Uses of Different Types of Microgreens
Microgreens offer a burst of vibrant flavors and textures that can elevate any dish they are added to. Different types of microgreens have distinct tastes that can range from peppery to sweet, adding depth and complexity to your culinary creations.
For example, peppery arugula microgreens can bring a spicy kick to salads or sandwiches, while the delicate and slightly nutty flavor of sunflower microgreens pairs beautifully with avocado toast or as a garnish for soups. Experimenting with various types of microgreens allows you to discover new flavor combinations and enhance the visual appeal of your dishes.
Incorporating radish microgreens into Asian-inspired stir-fries can provide a refreshing crunch and a hint of spiciness, while using basil microgreens in pasta dishes adds a fresh herbal note that complements the richness of the sauce. The versatility of microgreens makes them suitable for both savory and sweet dishes, offering endless possibilities for creative culinary exploration.
Incorporating Microgreens into Salads, Sandwiches, Smoothies, etc.
Microgreens are not only nutritious but also versatile in their applications across different meal categories. Adding a handful of colorful microgreens to salads not only enhances the visual presentation but also introduces various flavors and textures that can take your salad from ordinary to extraordinary.
The tender leaves of microgreens make them an ideal topping for sandwiches, providing an additional layer of freshness and crispness that complements the other ingredients. Smoothies offer another creative way to incorporate microgreens into your diet seamlessly.
Blending mild-tasting varieties such as pea shoots or broccoli microgreens with fruits like bananas or berries creates a nutrient-packed smoothie that is both refreshing and nourishing. The vibrant colors of microgreens can also be used as decorative garnishes on top of various dishes like omelets or soups, adding a pop of color and flavor that elevates the overall dining experience.
Troubleshooting Common Issues

Leaf Discoloration or Wilting: Unveiling the Telltale Signs
Leaf discoloration or wilting in microgreens can be concerning, but it is often a symptom of underlying issues that can be addressed with proper care. Yellowing or browning of leaves may indicate nutrient deficiencies, such as lack of nitrogen or iron. To remedy this, consider adjusting your fertilizer regimen to ensure a balanced mix of essential nutrients for healthy growth.
Overwatering can also lead to leaf discoloration, as it causes root rot and affects nutrient uptake. Ensure proper drainage in your growing trays and allow the soil to dry slightly between watering sessions.
In some cases, leaf discoloration could be a sign of pests infestation. Inspect your plants closely for any signs of insects and treat them promptly with natural remedies.
Leggy Growth: Shedding Light on Lack of Illumination
Leggy growth in microgreens occurs when they stretch out excessively in search of light, resulting in weak stems and sparse foliage. This phenomenon commonly happens when microgreens are grown in low-light conditions or placed too far from a light source. To prevent leggy growth, ensure your microgreens receive adequate light intensity by placing them under grow lights or near a bright window with ample sunlight exposure.
Rotate the trays regularly to promote even light distribution and encourage sturdy growth patterns. If leggy growth persists despite these efforts, consider adjusting the duration of light exposure to mimic natural daylight cycles for optimal development.
Mold or Fungal Growth: Navigating the Damp Dilemma
Mold or fungal growth in the growing medium can pose a threat to the health and vigor of your microgreens if left unchecked. Excessive moisture combined with poor ventilation creates ideal conditions for mold spores to thrive and spread rapidly throughout the trays. To combat mold infestations, ensure proper air circulation around your plants by using fans or opening vents in your growing area.
Avoid overwatering your microgreens and opt for bottom watering methods to prevent excess moisture on foliage surfaces. If you notice any signs of mold or fungus, promptly remove affected plants and adjust your watering routine accordingly to restore balance within your growing environment.
Advanced Techniques and Varieties

Exploring Unique Varieties of Microgreens
Delving into the world of microgreens opens up a realm of possibilities beyond the traditional choices. Unique varieties such as shiso, sorrel, and red amaranth offer exotic flavors and vibrant colors to elevate your culinary creations. Shiso microgreens bring a distinct basil-like taste with hints of citrus and cinnamon, perfect for adding a fresh twist to Asian-inspired dishes.
Sorrel microgreens provide a tangy, lemony flavor that pairs well with seafood or salads. Red amaranth microgreens boast a striking magenta hue and a mild earthy taste, making them not only visually appealing but also delicious in salads or garnishing dishes.
Conclusion
Embarking on the journey of growing your own microgreens is not just about cultivating tiny plants; it’s about nurturing a connection to nature and savoring the joy of harvesting your own fresh produce. By exploring advanced techniques and unique varieties of microgreens, you expand your culinary horizons while reaping the benefits of nutrient-dense greens at your fingertips.
Embrace the creativity in experimenting with different flavors and textures that these miniature powerhouses offer, knowing that each tray of microgreens you grow is a testament to your dedication to health and sustainability. Let these vibrant little plants inspire you to embark on further adventures in gardening and cooking, sparking joy and abundance in every harvest.