
Intro
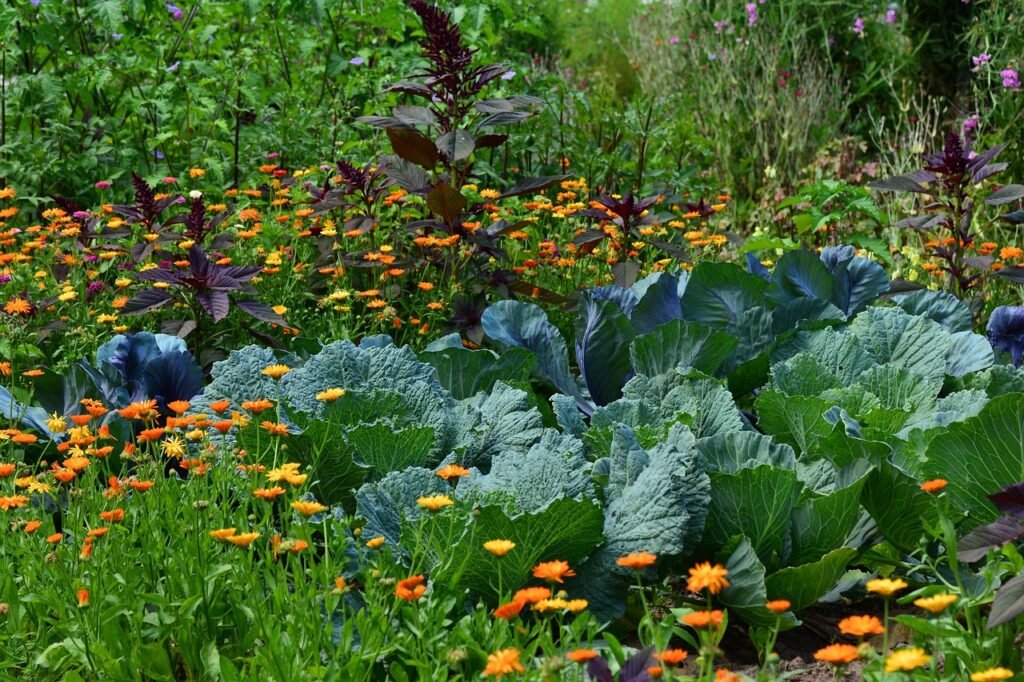
If you’ve ever dreamt of creating an abundant, self-sustaining oasis in your own backyard, permaculture gardening could be the answer. By harnessing natural processes and using eco-friendly techniques, you can turn your garden into a thriving food forest that provides for you all year round.
Understanding the Concept of Permaculture Gardening

Permaculture gardening offers an innovative and sustainable solution for those looking to bring an ecological balance to their home gardens. The term itself, permaculture, signifies ‘permanent culture,’ which was devised in the 1970s by two visionary Australian ecologists, Bill Mollison and David Holmgren. This pioneering concept marries traditional farming practices with an insightful understanding of modern ecological principles.
The objective behind permaculture gardening is to engineer efficient, self-sufficient systems that align seamlessly with natural patterns and cycles. It is the creation of agricultural ecosystems that mimic the harmony and sustainability of nature. In essence, it involves designing a self-sustaining environment where every element benefits and supports the others. It’s not just about growing food, but creating a symbiotic relationship between the soil, plants, insects, animals, and humans.
Permaculture is also about diversity. In a traditional garden, you might plant rows of a single vegetable. In a permaculture garden, the goal is to have as many different plants and animals as possible to create a robust, resilient system.
This innovative gardening approach goes beyond simply growing food. It seeks to nurture and preserve the entire ecosystem and is as much about lifestyle and philosophy as it is about practical horticulture. It encourages us to consider the impact of our gardening practices on the broader environment and to take steps to minimize our ecological footprint.
The beauty of permaculture gardening is that it can be applied on any scale, from small urban spaces to large rural farms, and everything in between. With its focus on sustainable and regenerative practices, permaculture gardening could be the answer to creating a lasting, beneficial relationship with your local environment.
The Three Core Ethics of Permaculture

Permaculture’s practice is anchored by a trilogy of fundamental principles, serving as a moral compass that guides decision-making and actions within the garden and beyond. These three ethics are Earth Care, People Care, and Fair Share.
Earth Care embodies the commitment to the preservation and rejuvenation of our planet. It’s about respecting and cherishing every life form and safeguarding the natural resources that sustain them. It implies creating an environment that not only benefits the garden but also the broader ecosystem. From the smallest soil microorganisms to the vast skies above, every element of nature should be treated with respect and consideration.
People Care is the second ethic, emphasizing the creation of supportive and resilient communities. In the context of permaculture, it’s about designing environments that meet human needs and contribute to wellbeing. This ethic calls for practices that foster strong community ties, promote self-reliance, and ensure every person’s needs are met in a sustainable way. It’s about recognizing that humans are an integral part of the ecosystem and should coexist harmoniously with nature.
Finally, Fair Share serves as a guiding principle for resource use and distribution. It encourages permaculture practitioners to limit their consumption and use resources in a manner that’s mindful of the needs of others and future generations. The ethic of Fair Share also encompasses the idea of redistributing surplus – whether it’s garden produce, seeds, or knowledge – to benefit the wider community.
These ethics not only offer a sustainable approach to gardening but also a philosophical framework for living in harmony with nature and each other. Understanding and embracing these principles is a significant step toward successful permaculture practice and creating a sustainable future for all.
Benefits of Permaculture for the Everyday Gardener

Integrating permaculture into your regular gardening practices offers an array of benefits that go beyond mere aesthetics. One of the most significant advantages is the enhancement of biodiversity within your backyard ecosystem. A diverse garden is not only visually appealing but also more resilient to pests, diseases, and varying weather conditions. A variety of plant species means a variety of habitats for beneficial insects, birds, and other wildlife, thus creating a vibrant, balanced ecosystem right at your doorstep.
In addition to boosting biodiversity, permaculture gardening can lead to improved soil health. Permaculture principles promote the nurturing of soil, fostering a rich environment teeming with beneficial microbes, insects, and worms. The result is fertile, nutrient-dense soil that provides the perfect growing medium for your plants.
One of the cornerstones of permaculture is the reduction, and often elimination, of artificial inputs. By encouraging the use of compost, green manures, and other organic matter, permaculture negates the need for chemical fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides. This not only results in healthier, more nutritious produce but also ensures a safer environment for the gardener and local fauna. Furthermore, it cuts down on the monetary investment typically required for garden maintenance, thus making permaculture an economically savvy choice as well.
Permaculture also brings a greater sense of satisfaction to gardening. It’s about more than just growing plants; it’s about cultivating a relationship with nature, and contributing to a healthier planet. Seeing the fruits of your labor flourish in a system designed to be self-sustaining and environmentally friendly can be immensely rewarding.
Finally, permaculture can transform the way you think about and interact with your garden. Instead of viewing it as a separate entity, you’ll start to see it as an extension of your home – a living, breathing entity that needs care and respect, but also provides nourishment and beauty. This shift in perspective can be deeply enriching and inspire a greater appreciation for the intricacies and wonders of the natural world.
Practical Permaculture Techniques for Your Garden
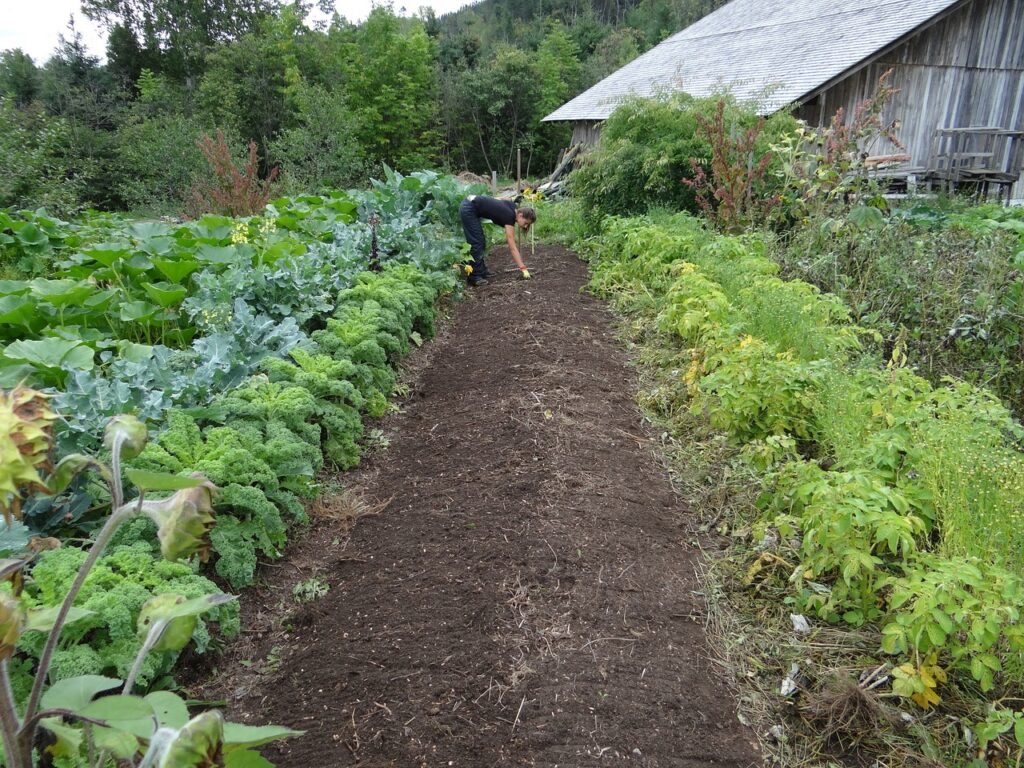

Implementing permaculture in your garden doesn’t have to be overwhelming or complicated. There are several simple and effective methods you can apply to start reaping the benefits of this eco-friendly approach. Here are a few practical techniques to help you get started:
Companion Planting: This involves growing different plants close together for mutual benefit. Certain plant combinations can improve growth, deter pests, and enhance flavor. For instance, growing tomatoes with basil not only helps ward off pests but can also enhance the flavor of your tomatoes.
Using Perennials: Consider incorporating a variety of perennial vegetables into your garden. Unlike annuals that need to be replanted each year, perennials come back year after year, providing a sustainable source of food and habitat for local wildlife.
Stacking: This refers to using vertical space to increase productivity. By growing plants at different heights, you can maximize your garden’s output without requiring additional ground space.
Natural Pest Management: Instead of using chemical pesticides, permaculture advocates for natural methods of pest control. This can involve encouraging beneficial insects, birds, and other creatures that prey on garden pests. Plants like marigolds, for instance, can deter harmful insects while attracting beneficial ones.
Sheet Mulching: Also known as lasagna gardening, this method involves layering organic materials on the garden surface to suppress weeds and improve soil fertility. It’s an excellent way to recycle kitchen scraps and yard waste into a rich, productive growing medium.
Rainwater Harvesting: This technique involves capturing and storing rainwater for later use in the garden. It’s an efficient way to conserve water and reduce dependence on municipal sources.
Implementing these techniques will help you create a diverse, productive, and resilient garden. It may take a little time and patience to see the full benefits, but the results – a lush, healthy, and eco-friendly food forest – are well worth the effort. Remember, the key to successful permaculture is observation and adaptation. So, take the time to learn about your garden’s unique conditions and needs, and adjust your methods accordingly.
The Transformation from Conventional Gardening to Permaculture
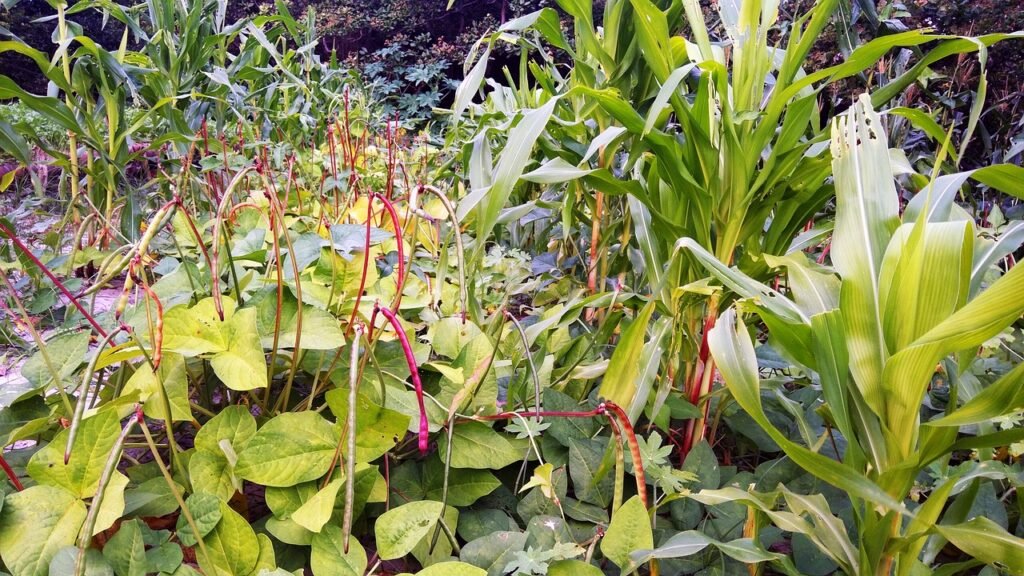

Embracing permaculture doesn’t mean a complete upheaval of your established gardening habits. Instead, think of it as an evolutionary journey where you gradually blend in permaculture principles with your existing practices. The initial phase should be focused on keenly observing and understanding your garden. Identify the various microclimates within your garden space, understand the type of soil you are working with, and acquaint yourself with the local flora and fauna.
In the beginning, you may wish to experiment with some of the simpler permaculture techniques. Companion planting, for instance, can be a good starting point. This strategy involves growing different plants in proximity for mutual benefit. For example, planting basil alongside tomatoes not only deters pests, but it also enhances the taste of your tomatoes. Another accessible technique is mulching. Using organic materials such as leaves, straw, or compost to cover your garden soil can suppress weeds, retain moisture, and enrich soil fertility.
As you grow more comfortable with these introductory practices, you can start integrating more complex techniques into your gardening routine. For instance, you might start incorporating more perennial plants into your landscape, which return year after year and often require less maintenance than annuals. Or you could explore stacking, a method of growing plants at different levels to increase yield without expanding the footprint of your garden.
The transition from traditional gardening to permaculture is a journey, not a destination. It’s about gradual improvement and adaptation rather than instant perfection. Along the way, you may face challenges and setbacks, but remember, these are opportunities for learning and growth. Stay patient, remain curious, and enjoy the journey of transforming your garden into a more sustainable and abundant space.
Unleashing the Power of Permaculture in Your Backyard

Stepping into a permaculture garden is a unique experience. It’s akin to entering a thriving, self-sustaining oasis where nature’s bounty is available at your fingertips. The transformation of your backyard into a sustainable food forest is an inspiring journey that begins with an appreciation for the environment and ends with the harvest of homegrown, eco-friendly produce. Imagine the satisfaction of enjoying fruits, vegetables, and herbs fresh from your backyard, the taste amplified by the knowledge of their organic, sustainable cultivation. The power of permaculture allows you to cultivate a garden that aligns with natural cycles, contributing not only to your kitchen but also to the overall health of the ecosystem. In essence, by adopting permaculture, you’re not just gardening, but actively participating in a movement that fosters environmental respect and sustainability. Remember, every plant you grow, every compost heap you build, and every rainwater barrel you fill contributes to a more sustainable future. So, as you venture into the world of permaculture, relish the journey and look forward to the abundant rewards awaiting in your transformed backyard. With permaculture, your garden becomes more than just a space for growing plants; it evolves into a vibrant ecosystem, a haven for biodiversity, and a testament to the beauty of sustainable living.




One thought on “Transform Your Garden into a Food Forest with Permaculture”