Growing strawberries for beginners
Introduction
The Joy of Growing Your Own Strawberries
Embarking on the journey of growing your own strawberries is a rewarding experience that offers a sense of accomplishment like no other. The satisfaction of nurturing a small plant into producing succulent, vibrant berries that burst with flavor is truly unparalleled. Each step in the process, from planting the tiny seedlings to delicately harvesting the ripe fruits, imbues a newfound appreciation for nature’s wonders and the cycle of growth.
Choosing the Right Strawberry Variety for Beginners
One crucial aspect that sets beginners up for success in strawberry cultivation is selecting the appropriate variety to suit their skill level and climate conditions. For novices venturing into this delicious endeavor, it’s recommended to opt for hardy and easy-to-grow varieties that are forgiving of minor mistakes or fluctuations in care routine.
Varieties such as ‘June-bearing,’ ‘Everbearing,’ or ‘Day-neutral’ offer distinct advantages based on their fruiting patterns and maintenance requirements, allowing beginners to tailor their choice to fit their gardening goals and available time commitment. By choosing wisely at the outset, beginners can set themselves up for a bountiful harvest and an enjoyable learning experience as they delve into the world of strawberry cultivation.
Introduction

Growing your own strawberries can be a truly rewarding experience that brings joy and satisfaction unlike any other. There is something magical about tending to these delicate plants, watching them flourish, and eventually being able to harvest plump, juicy berries right from your backyard. The process of nurturing strawberries from tiny seeds or seedlings into bountiful fruit-bearing plants is not only fulfilling but also educational, as you learn about plant care and the natural cycles of growth.
Brief Overview of the Joy and Satisfaction
The joy of growing strawberries extends beyond just the act of cultivation; it encompasses the entire journey from planting to harvest. Witnessing the first delicate blooms emerge from the green foliage, knowing that they will eventually transform into sweet fruits bursting with flavor, creates a sense of anticipation and wonder. As the berries ripen under the warm sun, each vibrant red gem becomes a symbol of your hard work and dedication paying off.
Importance of Choosing the Right Strawberry Variety for Beginners
For beginners venturing into strawberry cultivation, selecting the right variety is crucial for success. Different types of strawberries have unique characteristics such as growth habits, fruiting seasons, and flavor profiles. June-bearing varieties produce a single large crop in late spring or early summer, making them ideal for those looking for a concentrated harvest period.
Everbearing varieties bear fruit throughout the growing season with smaller yields per flush, providing a more extended picking timeframe. Day-neutral varieties offer a balance between these two types by continuously producing fruit regardless of day length.
Understanding these distinctions allows beginners to choose a variety that aligns with their preferences and gardening goals. By selecting an appropriate strawberry type suited to their region’s climate and their available time commitment for maintenance, beginners can set themselves up for a successful growing experience right from the start.
Selecting a Suitable Location for Your Strawberry Patch
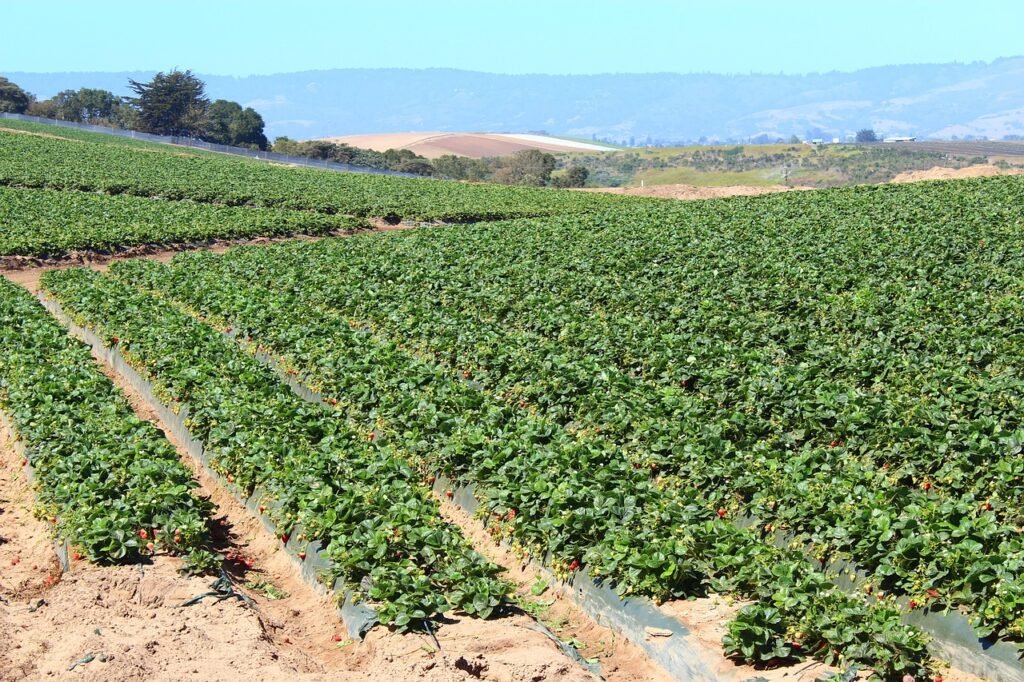

One of the crucial factors for successfully growing strawberries is choosing the right location for your patch. Strawberries thrive in full sun, so it is essential to select a spot that receives at least 6-8 hours of sunlight daily. A south-facing slope or an area that is not shaded by buildings or trees is ideal.
Sunlight exposure helps strawberries develop their signature sweetness and vibrant color. Additionally, ensure that the soil in the chosen location is well-drained to prevent waterlogging, which can lead to root rot and other diseases.
Understanding the Different Types of Strawberries
There are three main types of strawberries: June-bearing, everbearing, and day-neutral. June-bearing strawberries produce a single large crop in late spring or early summer, making them an excellent choice for those who want a bountiful harvest all at once for preserving or enjoying fresh.
Everbearing strawberries produce two to three crops throughout the growing season – typically in spring, summer, and fall. Day-neutral varieties are known for consistently producing fruit from spring through fall regardless of day length.
Testing and Amending Soil pH Levels for Optimal Strawberry Growth
Strawberries thrive in slightly acidic soil with a pH level ranging from 5.5 to 6.5. Before planting your strawberry patch, it is crucial to test the soil pH to ensure it falls within this ideal range.
You can easily test the pH of your soil using a home testing kit available at most garden centers or by sending a sample to a local agricultural extension service for more accurate results. If the pH level is too high (alkaline), you can lower it by incorporating elemental sulfur into the soil.
Conversely, if the pH is too low (acidic), you can raise it by adding lime. Maintaining the correct soil pH is essential for maximizing nutrient availability and promoting healthy strawberry growth.
Adding Organic Matter such as Compost or Aged Manure to Improve Soil Structure
In addition to adjusting the soil pH, enriching your strawberry patch with organic matter like compost or aged manure is vital for creating a fertile growing environment. Organic matter not only improves soil structure by enhancing drainage and aeration but also provides essential nutrients for robust plant growth. When preparing your strawberry bed, incorporate a generous amount of compost or well-rotted manure into the top few inches of soil using a shovel or tiller.
This organic amendment will promote beneficial microbial activity in the soil, which aids in breaking down nutrients and making them more accessible to your strawberry plants. Regularly replenishing organic matter throughout the growing season will help sustain healthy plant growth and bountiful harvests.
Planting Strawberries
Choosing between Planting Bare-Root Crowns or Seedlings
When it comes to planting strawberries, beginners often face the decision of whether to start with bare-root crowns or seedlings. Bare-root crowns are dormant plants with exposed roots that are typically less expensive and easier to handle.
They are a popular choice for those looking to establish a strawberry patch on a budget. On the other hand, seedlings are young plants that have already started growing and may provide a quicker yield compared to bare-root crowns.
Seedlings can be more convenient for beginners who want to see results sooner rather than later. In making your decision, consider the time of year you plan to plant as bare-root crowns are usually available in early spring while seedlings can be planted throughout the growing season.
Additionally, think about your level of experience and how much time you can dedicate to caring for your strawberries. Both options have their advantages, so choose based on what aligns best with your preferences and gardening goals.
Proper Spacing and Depth for Planting Strawberries in Rows or Mounds

Once you’ve decided whether to plant bare-root crowns or seedlings, the next crucial step is ensuring proper spacing and depth for planting your strawberries. Whether you opt for rows or mounds will depend on personal preference and available space in your garden.
For row planting, space each plant about 12-18 inches apart with rows spaced 2-3 feet apart. This layout allows adequate airflow between plants and makes maintenance tasks like weeding and harvesting more manageable.
If you choose mound planting, create raised beds or hills where strawberries can spread out comfortably. Plant each strawberry 8-12 inches apart within the mounds, ensuring that crowns sit at ground level for optimal growth.
Proper spacing is essential as it prevents overcrowding, promotes healthy root development, and encourages better fruit production. Remember that good spacing not only benefits individual plants but also improves overall yield and fruit quality in your strawberry patch.
Watering for Healthy Strawberries
Proper watering is essential for the success of your strawberry plants. To maintain healthy growth and abundant fruit production, it is crucial to establish a regular watering schedule. Strawberries have shallow root systems, so they need consistent moisture to thrive.
However, overwatering can lead to root rot and other fungal diseases, so it’s important to strike a balance. One effective way to water strawberries is to provide around 1-1.5 inches of water per week, either through rainfall or irrigation.
During hot and dry periods, you may need to increase the frequency of watering to prevent the soil from drying out completely. To avoid waterlogging the soil, consider using a drip irrigation system or watering early in the day so excess moisture can evaporate before evening.
Mulching for Weed Suppression and Moisture Retention
Mulching is a beneficial practice in strawberry cultivation that serves multiple purposes. By spreading a layer of straw or pine needles around your plants, you can suppress weed growth by blocking sunlight from reaching weed seeds and preventing them from germinating. This helps eliminate competition for nutrients and resources that strawberries need to thrive.
In addition to weed suppression, mulching plays a crucial role in retaining moisture in the soil. The layer of mulch acts as insulation, reducing evaporation from the soil surface and helping maintain consistent moisture levels around the strawberry plants.
This is especially important during hot summer months when dehydration can hinder plant growth and fruit development. Furthermore, mulching helps prevent fruit rot by keeping strawberries off the damp ground and reducing contact with soil-borne pathogens.
Fertilizing for Fruitfulness
One of the key steps in successfully growing strawberries is providing them with the proper nutrients they need to thrive and produce an abundance of fruits. When it comes to fertilizing strawberries, it is essential to use a balanced fertilizer that is high in phosphorus.
Phosphorus plays a crucial role in promoting flowering and fruit production in plants, making it particularly important for strawberry plants. Look for a fertilizer specifically formulated for berries or fruits, with an N-P-K ratio that emphasizes phosphorus (the middle number).
To apply the fertilizer, it’s best to follow the instructions on the product packaging carefully. Generally, you’ll want to apply the fertilizer around the base of the plants, being careful not to let it come into direct contact with the leaves or stems.
Fertilize your strawberries in early spring as they start actively growing and again after the first flush of fruiting. Over-fertilizing can lead to excessive foliage growth at the expense of fruit development, so be sure to use fertilizers sparingly but consistently throughout the growing season.
Pruning for Healthier Plants
In addition to proper fertilization, pruning is another important aspect of caring for your strawberry plants. Regularly pruning runners (long stems that develop from mother plants) helps redirect energy back into fruit production rather than vegetative growth. By removing these runners, you encourage your strawberry plants to focus their resources on developing larger and juicier fruits.
Furthermore, pruning old leaves is essential for maintaining plant health and vigor. Old leaves are more prone to diseases and pests, so removing them not only improves air circulation around the plant but also reduces potential sources of infection.
When pruning old leaves from your strawberry plants, make sure to use clean and sharp gardening shears to make precise cuts without causing unnecessary damage. Aim to prune throughout the growing season as needed, focusing on removing any yellowing or damaged foliage.
Pest Control
Identifying Common Pests
Strawberry plants are susceptible to various pests that can threaten your harvest. Slugs are a common enemy of strawberries, leaving behind slimy trails and devouring leaves and fruits. Birds are another notorious offender, pecking at ripe berries and causing significant damage.
Aphids, small insects that feed on plant sap, can also infest strawberry plants, weakening them and reducing fruit yield. It is crucial for beginners to be vigilant in identifying these pests early on to prevent extensive damage to their strawberry crop.
Implementing Natural Pest Control Methods
One effective method of pest control in strawberry cultivation is companion planting with marigolds. Marigolds emit a scent that repels many harmful insects, including aphids and nematodes, thereby protecting neighboring strawberry plants. Planting marigolds around the perimeter of your strawberry patch or interspersing them among the strawberry plants can help deter pests naturally.
Additionally, using row covers made of lightweight fabric can act as a physical barrier against birds and other flying pests while allowing sunlight and water to reach the plants unhindered. Row covers should be securely anchored to prevent pests from gaining access underneath them and causing damage to the strawberries.
Harvesting Tips

The Art of Knowing When Strawberries are Ripe
When it comes to harvesting strawberries, timing is crucial. Ripe strawberries will have a deep, vibrant red color all over the fruit, with no white or green areas remaining. Size is also a good indicator – ripe strawberries will be plump and evenly-shaped.
In terms of taste, a ripe strawberry should be sweet with a slight tanginess and a fragrant aroma. It’s essential to wait until the berries are fully ripe before harvesting to enjoy them at their peak flavor.
Gently Picking for Prolonged Freshness
To ensure your freshly harvested strawberries stay fresh longer, it’s best to pick them with their stems intact. Gently grasp the stem right above the berry and pull it off the plant with a slight twisting motion. Avoid pulling on the berry itself as this can cause damage and reduce its shelf life.
Handle the strawberries carefully to prevent bruising, which can lead to faster spoilage. Store harvested berries in a single layer in a shallow container in the refrigerator for up to 5 days for optimal freshness.
Conclusion
Growing strawberries can be a rewarding experience for beginners seeking to cultivate their own delicious fruits at home. By following proper planting techniques, providing adequate care throughout the growing season, and mastering the art of harvesting ripe berries, you can savor the sweet taste of success in your strawberry patch.
Remember that patience and attention to detail are key factors in achieving bountiful harvests of juicy strawberries year after year. Embrace this journey into strawberry cultivation with enthusiasm and optimism – each berry picked represents your dedication and love for nurturing nature’s bounty.