Intro
Raised bed gardening has gained immense popularity among both novice and experienced gardeners. This sustainable and efficient gardening technique offers several advantages and can be a fun, rewarding experience.
Understanding Raised Bed Gardening: What It Is and Why It’s A Great Option
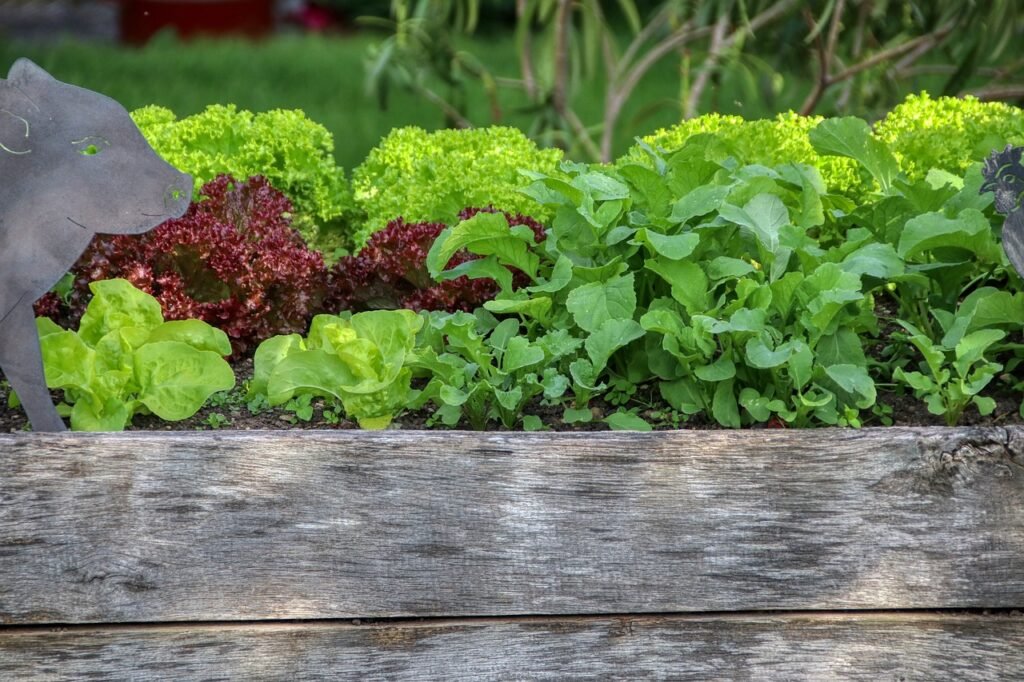

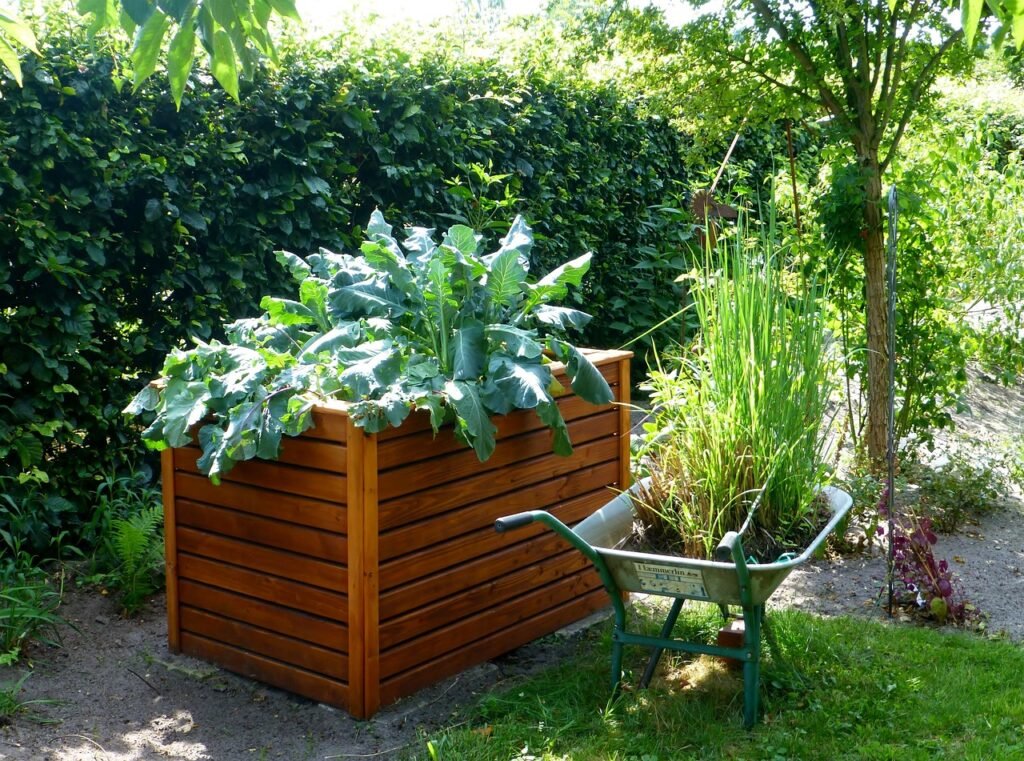
Raised bed gardening is a unique method where plants are cultivated in elevated soil structures referred to as “raised beds”. While these beds can vary in length or shape, they typically reside within a frame that’s around 3 to 4 feet in width. One of the major advantages of this gardening approach is the control it provides over the soil environment. This means you have the ability to tailor the soil composition specifically for the plants you intend to grow, ensuring they get the nutrients they need.
Additionally, the raised design improves soil drainage, which is beneficial for preventing water-logged roots and fostering healthy plant growth. At the same time, it helps prevent soil compaction, a common issue in traditional gardens that can hinder plant development.
Perhaps one of the most appealing aspects of raised bed gardening is its effect on the growing season. Given that the soil within raised beds is positioned above ground level, it warms up more quickly when spring arrives. This allows you to get a head start on your planting and extends the growing season. This means you’ll get to enjoy your homegrown vegetables, herbs, or flowers sooner than traditional ground gardening would allow.
The Best Wood for Raised Garden Beds: Durable and Eco-friendly Choices
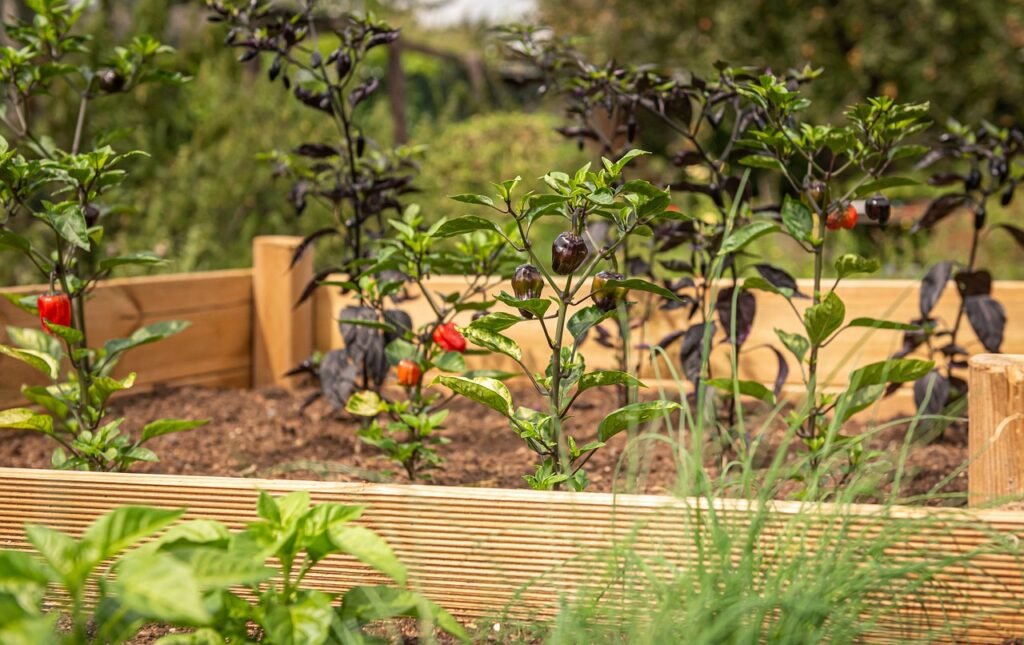

Selecting the right wood when constructing a raised garden bed is key for longevity and environmental safety. Certain types of wood, such as Cedar and Redwood, are renowned for their durability and natural resistance to both rot and pests. These characteristics make them highly sought after for such projects, however, they can be quite expensive due to their high-quality nature.
If you’re working on a budget, untreated Pine could be a suitable alternative. It’s not only more economical, but also has a decent lifespan, providing service for many growing seasons. It’s important to note though that Pine won’t last as long as Cedar or Redwood due to its lower resistance to decay.
Regardless of cost considerations, it’s vital to steer clear of pressure-treated wood when constructing your raised beds. This type of wood often contains potentially harmful chemicals which can seep into your garden’s soil over time. These substances can be detrimental to your plants, and can potentially pose health risks if the produce is consumed.
When making your wood selection, considering both the durability and potential environmental impact is key for a safe and successful raised bed garden. Here is more information on the best options for your raised beds https://earthenink.com/index.php/2024/02/17/266/
How to Build Your Own Raised Garden Bed: A Step-by-Step Guide

Creating a raised garden bed from scratch can be a fulfilling endeavor. The necessary materials include your preferred wood, galvanized screws, a drill, a saw, a tape measure, and a square. Begin by measuring and cutting your wood to the size you desire. Using your drill, assemble the bed’s frame by affixing the boards together at the corners with the galvanized screws. Make sure your screws are placed securely to ensure the sturdiness of your bed.
Once the bed frame is constructed, position it in the location you’ve earmarked for your garden. Take care to ensure the bed is level; an uneven bed can lead to water pooling in one area and not evenly hydrating your plants.
Next, it’s time to prepare your soil mixture. Raised bed gardening offers you the flexibility to customize your soil mix based on the plants you plan to grow. Generally, a good starting point is a combination of topsoil, compost, and other organic matter. This mix promotes a healthy growing environment packed with the necessary nutrients your plants will need.
Carefully fill the bed with your soil mixture. Be mindful not to overfill as this can lead to soil erosion when watering. Once the bed is filled, your handcrafted raised bed garden is ready for planting. You can now select and sow the seeds or seedlings of your chosen plants.
Remember, the success of your raised bed garden doesn’t stop at construction. Regular maintenance, including watering, replenishing with compost, and checking for pests, will ensure that your garden thrives. As you become more familiar with raised bed gardening, feel free to experiment with different plants and companion planting techniques to maximize your garden’s yield and enjoyment.
Choosing the Right Plants for Your Raised Bed Garden: What Works Best
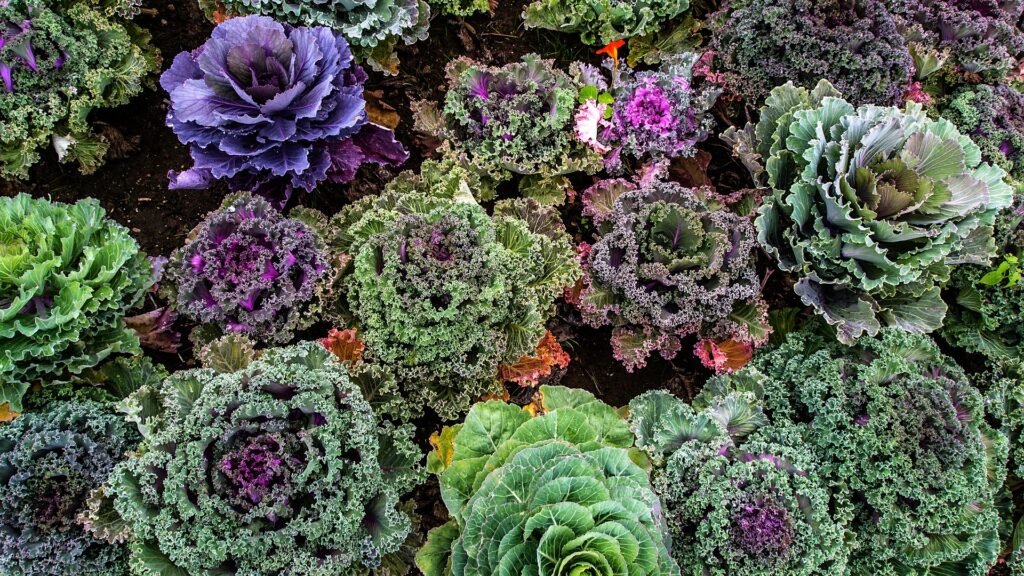

Raised bed gardening opens up a world of possibilities in terms of plant selection. Many gardeners choose to grow a variety of vegetables in their raised beds due to the optimal growing conditions. Plants like tomatoes, peppers, lettuce, and carrots are often very successful and provide a bountiful harvest. However, the opportunities do not stop at vegetables.
You can fill your raised beds with vibrant flowers, fresh herbs, or even fruit trees, depending on the size and depth of your beds. This variety not only adds aesthetic appeal to your garden, but also can offer different benefits to the overall health and productivity of your plants.
Companion planting is an effective strategy to consider when choosing your plants. This technique involves grouping certain plants together based on their mutual benefits. For instance, planting marigolds near your vegetables can help to ward off harmful pests. Similarly, growing basil alongside your tomatoes can actually enhance the flavor of the tomatoes.
When selecting the plants for your raised bed, consider factors like their growth habits, sunlight and water requirements, and their compatibility with other plants. It’s also worth considering plants that can deter pests, attract pollinators, or enrich the soil.
Keep in mind that the choices are limitless, and the beauty of raised bed gardening is that you can easily modify and adjust your planting strategy from season to season. Experimentation is part of the fun, and you may discover some unexpected, successful pairings along the way. So, explore, experiment, and enjoy the process of creating your unique raised bed garden.
Maintaining Your Raised Bed Garden: Tips for Success

Ensuring the ongoing success of your raised bed garden involves a number of maintenance tasks. Proper watering is paramount; however, it’s vital to understand that due to their elevated nature, raised beds tend to drain more rapidly than traditional gardens. This could necessitate more frequent watering sessions to keep your plants properly hydrated.
Incorporating compost into your garden beds on a regular basis is another key factor in maintaining a thriving garden. Compost enriches the soil with vital nutrients that plants need to grow strong and healthy. Not only does it promote plant growth, but it also enhances the soil’s ability to retain water, which can be beneficial for raised beds due to their enhanced drainage.
Keeping a vigilant eye out for potential pest infestations is also crucial. Implement organic pest control measures whenever possible to ward off insects and other pests that could harm your plants. Organic pest control methods are more environmentally friendly and pose less risk to the health of your plants and anyone consuming your produce.
Lastly, practice crop rotation in your raised bed garden. This involves changing the position of your crops each growing season. This technique helps to prevent the spread of diseases and pests that might be specific to a certain type of plant. Additionally, it contributes to the maintenance of soil health, as different plants have different nutrient requirements and can help keep the soil balanced.
Remember, while building your raised bed garden is a significant first step, the journey doesn’t stop there. Consistent care and maintenance are necessary to ensure your raised bed garden flourishes, providing you with a bountiful harvest and a rewarding gardening experience.